Evan's, Ivan's, Ricky's and Tommy's
WILLIAMS-REHAB CENTER 🍺
/
Brewing/
Menu/
ReferencesBlog 4: THE SPONGEBOB (Fructose beverage)
Research by Ivan
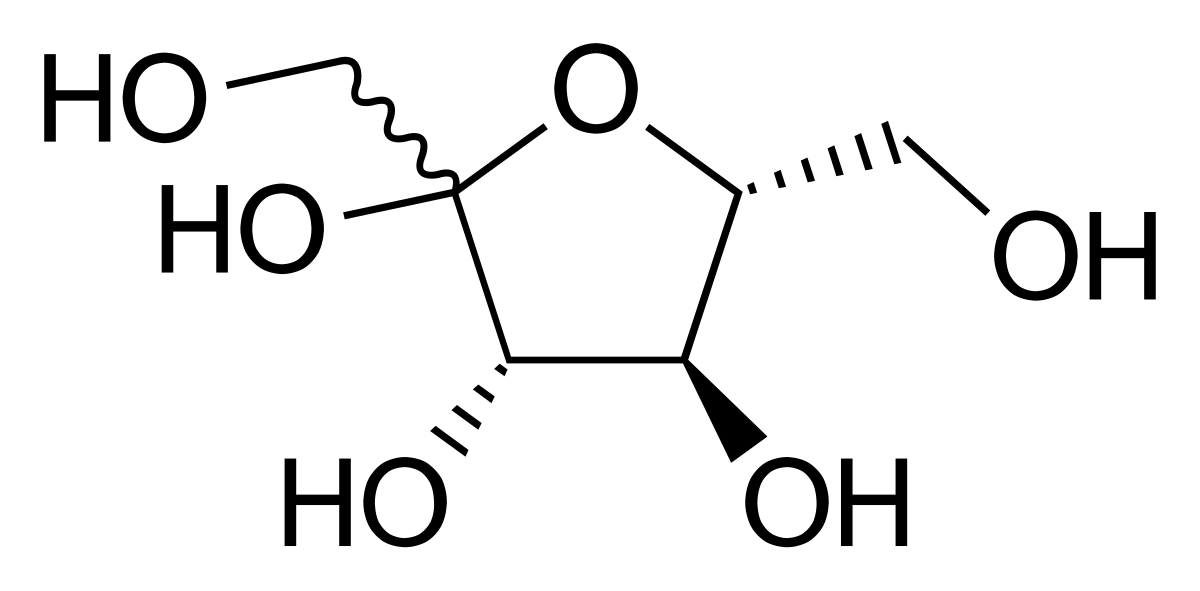
Spongebob is a mocktail derived from the sugar fructose through pineapple juice. It is a 6-carbon atom that contains hydroxyl and ether groups that its IUPAC name can identify: (3S,4R,5R)-1,3,4,5,6-Pentahydroxyhexan-2-one. Fructose formula is C6H12O6
During the discovery process of using fructose, quantitative data including its weight, 248.3 g and fermentation time of 2 weeks. Fructose produced 0 carbon dioxide. However, we observed an unexpected smell; the fructose emits a soy sauce-like odour instead of the fruity odour typical in pineapples. The mocktail also produced a soft yellow colour readily soluble due to the density difference. It is also important to note how fructose has the lowest energy production. Thus, it is more difficult for fructose to undergo fermentation.
In creating our pineapple alcohol, its fermentation process is complicated. In our procedure, no alcohol was produced, becoming a mocktail for everyone to enjoy. This is due to our ratios. At our establishment, we stand by our ratios. One 250 ml of pineapple contains around 30 grams of sugar. Thus, our fermentation involved two cans of pineapple juice to reach 62.5 grams of sugar combined with 250 ml of water and yeast. However, no alcohol was produced. We can conclude no alcohol was produced due to Bromelain in pineapple juice. A natural enzyme is known as a proteolytic enzyme found in pineapple juice. This enzyme can mainly break down proteins. As such, the enzyme potentially denatured the yeast’s protein to ferment the fructose in alcohol. Nevertheless, if we want to make it into alcohol, we have potential solutions to fix it. As bromelain causes the yeast protein to denature, our solutions can prevent the bromelain from denaturing the enzymes through heat treatment and yeast. To contain bromelain from denaturalising enzymes, we can use pasteurisation that follows the principles of heating the pineapple juice to a specific temperature for a short period to inactivate bromelain. Another source for providing fermentation is the type of yeast used. For example, different yeast strains may be more tolerant to external factors affecting their fermentation.
References
BROMELAIN: Overview, Uses, Side Effects, Precautions, Interactions, Dosing and Reviews. (n.d.). WebMD. Retrieved June 13, 2023, from https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-895/bromelain
Fructose. (2017, August 28). American Chemical Society. Retrieved June 14, 2023, from https://www.acs.org/molecule-of-the-week/archive/f/fructose.html
Ndip, R. N., Akoachere, J. -F. K. T., Dopgima, L. L., & Ndip, L. M. (2001, January). Characterization of yeast strains for wine production. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 95, 209–220. https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:95:3:209
Phong, H. X., Klanrit, P., Dung, N. T. P., Thanonkeo, S., Yamada, M., & Thanonkeo, P. (2022, August 17). High-temperature ethanol fermentation from pineapple waste hydrolysate and gene expression analysis of thermotolerant yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 13965. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-18212-w
Why Does Yeast Ferment Glucose Faster than Fructose? (n.d.). Oculyze. Retrieved June 13, 2023, from https://www.oculyze.net/why-does-yeast-ferment-glucose-faster-than-fructose/